Squats mean "sucking down and exhale"? Expert reminds a breathing detail

【Text, Picture/Excerpt from the Practical Culture "Strength Squat", author Yaren Hoshger]
Suitable BreathWhen squats, the control of "like a punch in the stomach" is not enough. If you want to move the weight in a safe way, you still need to learn how to breathe properly. For a long time, muscle strength and medical experts in the field of physical education failed to teach appropriate breathing during weight training. Our core is like a ball of air, trying to strengthen the exterior and replace learning to increase internal pressure.
Experts in the field of muscle strength and medical care teach "sucking down and exhaling down" that is not a problem for light and numerous training exercises (for example: three sets and ten strokes are recommended). However, this breathing mechanism is not completely recommended when squatting. Can you imagine a Jianli player who squats for 1,000 pounds and spits out all his air when he stands up?
When our squats are heavy (for example, more than 80% of your maximum weight), it is recommended to take a big breath of air every time and hold it in before completing that action. Usually this type of breathing method is not required when you weigh multiple times, but when you squat more frequently, this is the breathing key, which must be prepared in advance and cooperate with the feeling of "like a punch in the stomach". This can make us very stable.
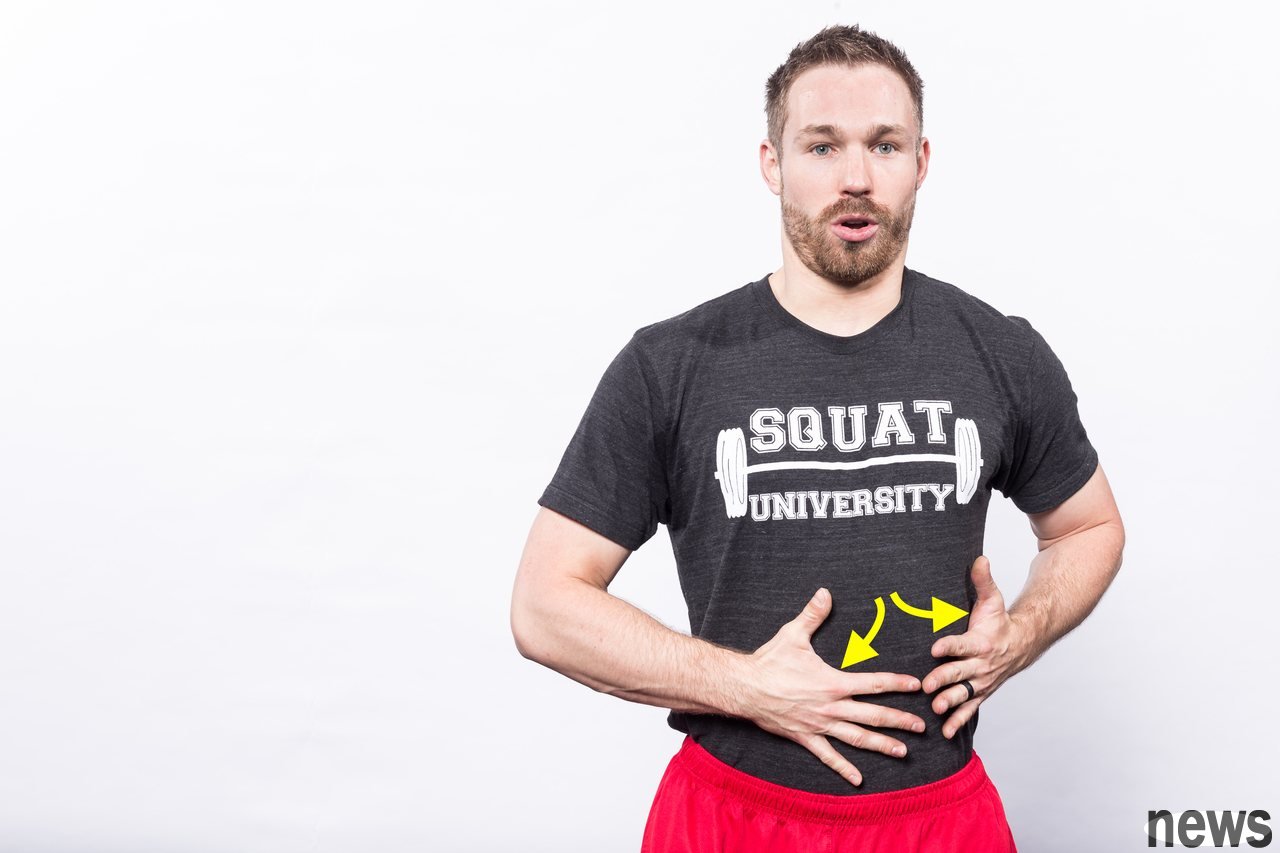
Learn how to breathe properly during squats, you can try this simple test below. Put one hand on the abdomen and the other hand on the waist (near the lower ribs), and take a deep breath now. If you breathe properly, you will feel your abdomen undulation, and you will also feel your lower ribs stretching to the side. Basically, you will feel the capacity changes in the core. When we take a deep breath, the septum below the lungs contracts and descends toward the abdomen.
If you inhale in a bad way, instead of the ups and downs of your chest, breathing in this way has little effect on increasing pressure in the abdominal cavity because the diaphragm is not fully utilized. Why is it so important to increase capacity?
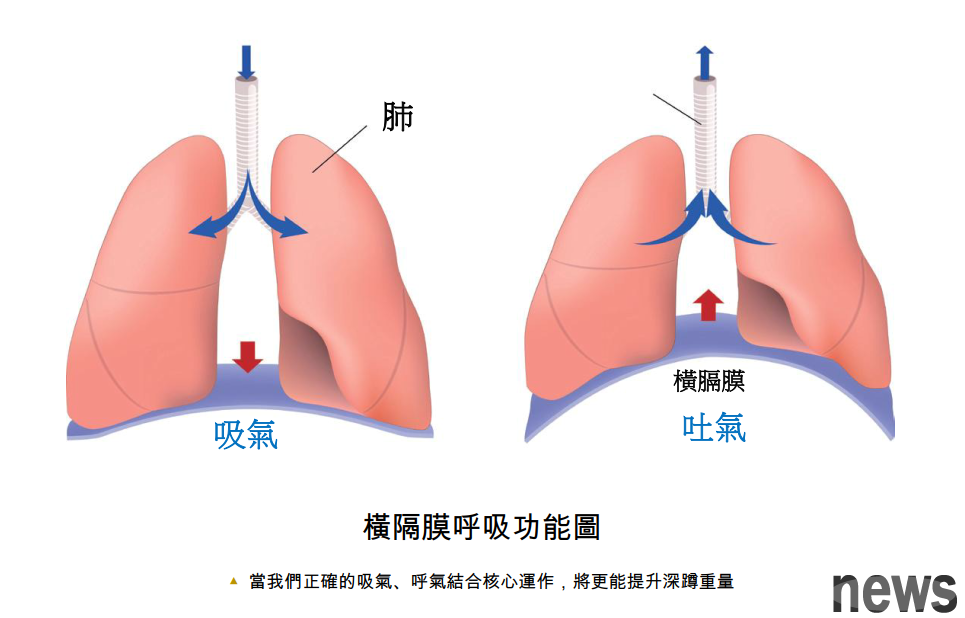
When we correctly inhale the air into the abdomen and apply core force, you will find something special. Put your hands on your abdomen again and take a deep breath again. After a deep breath, the core force feels like you are ready to take a punch from Microtison, combining this action to increase the abdominal pressure (abdominal pressure or IAP), because the capacity cannot be increased again. Research has shown that increasing abdominal pressure during calcification training is the most effective way to stabilize the lower back.
This needs to be done step by step. If we first put our core force and then try to take a deep breath, it will limit the pressure we can create. If the core is already pressed, the diaphragm cannot completely shrink and drop. Compared to the limitations caused by core force alone, increasing the abdominal pressure will make our lower back more stable.
To feel the core pressure and your overall strength, you can try the following simple test. Put the pin on your back and spit out all the gases in your lungs. Feel the feeling of stooping on your back. Then, take a deep breath and apply force to the core. Trying to create a 360-degree pressure at the core, it feels like wearing a tight suit. Remember, breathing must be stretched on the front, side and back of the core area. Have you noticed any difference?

Now you should feel that the stent on your back is much lighter. Can this strategy be used more reasonably to increase the weight of the squat? This is why strong weight and fitness pickers can carry huge weights in a squat without being folded in half.
When squatting, holding the air can easily increase the pressure. When we try to increase the limit, the breath will naturally occur. This maintenance force is called "the phenomenon of hard work." In this powerful way to maintain spinal stability, holding your breath is inevitable.
Use "working phenomenon" correctly, which means exhaling forcefully when rising to resist the airway closing. As we say, "sucking down and exhaling up", squat rising means using complete exhalation to make the pressure in the abdomen drop sharply.
When our abdominal pressure drops, spinal stability will decrease. This has nothing to do with our core efforts. When you exhale completely, stability will naturally drop immediately, and the harmful pressure will be transmitted to the small and fragile structure of the spine (intervertebral plates and straps). This is like the state where the air ejaculates out of the air ball too quickly. When the air ejaculates out of the air ball, the air ball becomes unstable in an instant. This is the same as our body principle.
However, if we keep the pressure on the ball opening through the force, only a small amount of air will leave the ball open, the ball will remain stable for longer. In order to maintain abdominal pressure and spinal stability, the body must completely stop exhaling. Conceptually, it's like we have to place our fingers in the air ball opening. There are several different methods that can be achieved. Some people with heavy weight use the air-holding method or slowly exhaling through the small holes in their lips to make a sneering sound. These two methods will keep the abdominal pressure of the entire process at a higher level.
It is recommended that when squatting, do not breathe more than a few seconds, so as to avoid significant increase in blood pressure, loss of consciousness and other cardiovascular damage risks. Although the effort (even if it lasts for a short period of time) is sure to increase the contraction pressure, it is very safe for a healthy athlete. For most people, blood pressure is rising regularly and harmless. Even so, be careful for the elderly and anyone with a history of medical care.

The so-called appropriate squat is focused on maintaining proper spinal stability. When we combine the coordination ability of our core muscles and harness the power of our breathing, this will allow our bodies to produce better states, move appropriately and safely lift larger weights.




