Who needs vitamin D? How much does it take to eat? In addition to eating, the sun can also be supplemented with the appropriate sunlight.

When the hot summer comes, it is very hot every day. Many people want to stay in the cold room every day and not leave the door. However, the suitable sunlight can help us promote the synthesis of vitamin D. At present, more and more literature is exploring the positive effects of vitamin D on many diseases, making it a new source of medical and nutritional circles in recent years.
According to the National Nutrition Survey, the national population generally has insufficient vitamin D intake and has been listed as one of the most prone nutrients that the national population lacks. It is believed that vitamin D plays a very important role in maintaining human health. Therefore, the National Health Administration has increased the recommended intake of vitamin D in the "Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs) Eighth Edition", hoping that the public can increase the standard for intake.
Today, the brand nutritionist of "Health Designer" will take you to know what is harmful to vitamin D!
Vitamin D's small fileVitamin D (Vitamin D) is a fat-soluble vitamin with a structure similar to sterols. It is mainly D2 and D3 in the human body. It has very little content but is an important nutrient for maintaining physical health! What is more special is that in addition to making vitamin D by food, it is also a vitamin that a few people can synthesize by themselves! There are two main ways to obtain vitamin D:
1. Vitamin D is called "sun vitamin" when the skin is irradiated by the sun. The reason is that when the skin is exposed to the sun, the 7-dehydrocolesterol (7-dehydrocolesterol) present on the skin surface will turn into previtamin D3 (Previtamin D3), and then turn into vitamin D3 (Vitamin D3, Cholecalciferol).
2. Food sources include vitamin D2 and D3 from different organisms: • Vitamin D2 (Vitamin D2, Ergocalciferol, methylol): exists in plants, yeast, fungi, etc.; Vitamin D3: exists in animal tissues
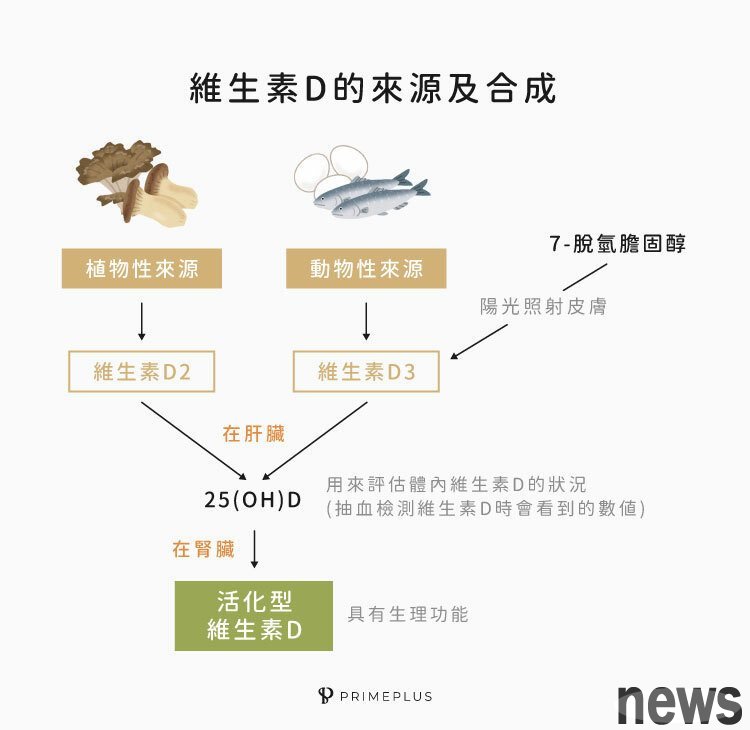
Neither vitamin D2 nor D3 have physiological activities, and it is necessary to undergo a transformation of the liver and kidneys in the body to become activated vitamin D with physiological functions. Therefore, if there is a problem with the liver or kidney, it is very likely to affect the activation of vitamin D in the body!
Physical functions of vitamin DThe role of vitamin D in human body is similar to that of steroids. It has many different physiological functions, mainly through a special receptor to adjust the functions of various organs in the body. Therefore, its function can be said to be spread throughout the body:
. Promote calcium absorption and regulate calcium phosphorus balance in the blood. Vitamin D can promote the calcium and phosphorus absorption rate in the kidney and kidney, and jointly maintain the calcium phosphorus balance in the blood with thyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone. Without vitamin D, only 10 to 15% of the calcines in the diet can be absorbed, and with the help of vitamin D, the absorption rate can reach 30 to 40%.
. Maintaining bones and teeth health Vitamin D can act on osteoblasts that are responsible for bone remodeling and help bone formation. Therefore, it is effective in preventing and improving bone relieving!
. It can affect cell differentiation, hyperplasia and growth of different organizations. Research has found that vitamin D has unique information transmission mechanisms in the human heart, brain, skin, muscles and immune system, which can affect the expression of cell genes, adjust cell differentiation and growth, and thus adjust physiological functions. In addition, studies have shown that this is the main reason for vitamin D to help prevent cancer!
. Protecting cardiovascular, kidney and other organs. As mentioned above, many organs contain vitamin D receptors. When the cells in these organs are damaged by diseases, oxidative pressures, vitamin D can adjust the physiological reactions in the body to protect our organ organ tissues.
. Participating in immune regulation Vitamin D can regulate immune cells, thereby preventing infection and autoimmune diseases (such as polydehyde sclerosis), and also adjusting inflammation response.
. Preventing respiratory infections
Vitamin D can enhance the respiratory tract's ability to resist bacteria, thereby maintaining respiratory health, and with the function of adjusting immunity, vitamin D has become one of the main research goals nowadays when COVID-19 is raging.
. Prevention and improvement of chronic diseases have been proven to improve many chronic diseases, including: hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, etc., and maintaining a good concentration of vitamin D in the body can also prevent the occurrence of these diseases!
The source of vitamin D1. Success is an important source of vitamin D in humans. The Ministry of Health recommends that you can expose your face, arms and other parts for exposure, but avoid direct sunlight. It is best to use before 10 am or after 2 pm (applicable for Taiwan). It is a time when there is sufficient sunlight but not the strongest. Do not apply anti-splenish breasts when exposed. After about 10 to 20 minutes, the body can synthesize a sufficient amount of vitamin D!
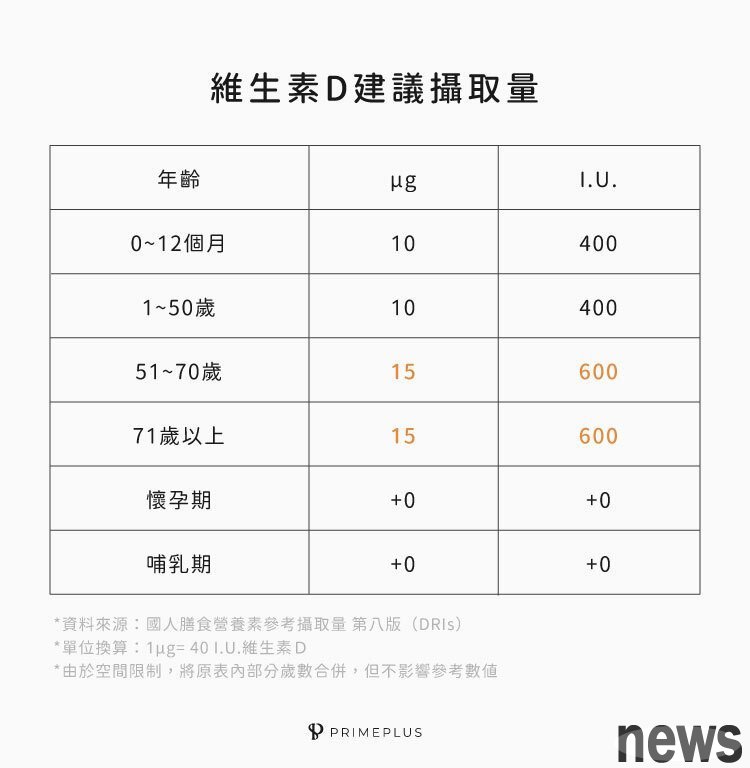
2. Food sources of vitamin D mainly come from animal foods, such as fish, eggs, liver, beef, etc., while plant-based sources include mushrooms, fungus, etc.. So how much does Vitamin D need to eat? We provide our recommended intake of vitamin D from the eighth edition of DRIs. We can use it as a reference when evaluating whether you need additional supplementation!
By detecting the 25(OH)D concentration in the blood, you can know the status of vitamin D in the body. Generally, ≧50 nmol/L is sufficient, while <30 nmol/L is lack. The lack of bone mineralization caused by vitamin D deficiency is "rispermia" in infants and "osomal mutation" in adults.
In addition, some special groups such as: the elderly, liver failure, those suffering from malabsorption, those taking glucocorticoid steroids, etc., may be due to reduced physiological functions, drug interactions, etc., and special considerations are needed to consider whether additional supplementation is needed!
After reading the vitamin D introduced above, do you think vitamin D is a very harmful nutrient? In addition to what we are familiar with, it can also be effective for many diseases and promote physical health. If most office workers who work indoors on weekdays or lack a Japanese group, they can also maintain their internal vitamin D through eating! If additional supplementation is required, the appropriate principle must be followed. Over-replenishing fat-soluble vitamins may cause harm. If you have any other questions, you must consult the doctor or nutritionist’s advice before replenishing it!




